高考英语大纲规定的24个语法梳理(十一)

1
概述
⒈ 引用或转述别人说的话时有两种方法:直接引述别人的原话,这叫做直接引语(direct speech), 一般直接引语前后要加引号。
如:Mr.Black said,“I'm busy.”布菜克先生说:“我 很忙”。(直接引语)
⒉ 用自己的话转述别人的话,叫间接引语(indirect speech),一般间接引语不用引号,而用宾语从句来表达。
Mr.Black said that he was busy.布菜克先生说他很忙。(宾语从句是间接引语)
⒊ 从上例看来,直接引语改为间接引语时,除将直接引语改为宾语从句之外,还须对直接引语中的人称和时态进行相应的变化,如上例直接引语中的I改成了he,am则改成了was。
现将由直接引语改为间接引语时应注意的问题分述如下:
2
当直接引语是陈述句时
直接引语如果是陈述句,变为间接引语时,用连词that引导(that在口语中常省去),that从句之前用say、tell等动词,从句中的人称、时态、指示代词、时间状语、地点状语等要作相应的变化。
⒈ 人称的变化
① 直接引语改为间接引语人称要相应的变化,把直接引语中的第一人称(如:I,me,my,mine,we,us,our,ours)变为与主句的主语相一致的人称。
如:He said,“I like it very much.”他说:“我非常喜欢它”。
→He said that he liked it very much.他说他非常喜欢它。(I改为he,it不变)
② 把直接引语中的第二人称(you,your,yours) 变为和主句的间接宾语(即 听话人,如无话人,可根据上下文的体会人为确定一个人称) 相一致的人称。
He said,"You told me this story.”他说:“你给我讲过这个故事。”
→He said that I had told him that story.他说我给他讲过那个故事。(You改为I,me改为him,told改为had told)
③ 直接引语中的第三人称(he,him,his,she,her,hers,it,its,they,their,theirs,them)变为间接引语时,人称不变。
He said to me,“She's left her book in your room”.他对我说:“她把书放在你的房间里去了。
→He told me that she had left her book in my room.他对我说她把书放在我的房间里(She's→she had,her不变,your→my)
⒉ 时态的变化
① 主句的谓语动词是一般过去时
如主句的谓语动词是一般过去时,直接引语变间接引语时,从句的谓语动词在时态方面要作相应的变化。直接引语改为间接引语时,动词时态相应变化如下:
He said,"I usually watch TV on Sunday.”他说:“我常在星期天看电视”。
→He said that he usually watched TV on Sunday.他说他常在星期天看电视。
He said,“I'm using the knife.”他说:“我正在用小刀。”
→He said that he was using the knife.他说他正在用小刀。
She said,“I have not heard from him since May.”她说:“自从五月份来我就没收到他的来信。”
→She said that she had not heard from him since May.她说自五月以来她就没收到他的来信。
He said,“I came to help you.”他说:“我来帮助你。”
→He said that he had come to help me.他说他来帮助我。
He said,“I had finished my homework before supper.”他说:“晚饭前我己做完了作业。”
→He said that he had finished his homework before supper.他说晚饭前他己做完了作业。
Zhou Lan said,“Ill do it after class.”周兰说:“下课后我就去做。”
→Zhou Lan said that she would do it after class.周兰说下课后她就去做。
He said,“I shall be doing my homework then.”他说:“那时我将正在做作业。”
→He said that he should be doing his homework then.他说那时他将正在做作业。
He said,“We shall have finished the work by that time.”他说:“我们将在那时以前完成工作。”
→He said that they should have finished the work by that time.他说他们将在那时前完成工作。
注意:直接引语如果是客观真理、名人名言、与一个具体的过去时间连用说明客观事实时,变为间接引语时,时态不变。
The teacher said,“The earth is round.”老师说:“地球是圆的。”
→The teacher said that the earth is round.老师说地球是圆的。
He said,"I was born in Shangdong in 1965.”他说:“我1965年生于山东。”
→He said that he was born in Shangdong in 1965.他说他1965年生于山东。
He said,“Columbus discovered America in 1492.”他说:“哥伦布在1492年发现了美洲。”
→He said Columbus discovered America in1492.他说哥伦布在1492年发现了美洲。
② 主句的谓语动词是现在时或将来时如果主句的谓语动词是现在时或将来时,直接引语变为间接引语时,时态一律不变
He says,“I finished the work.”他说:“我做完工作了。”
→He says that he finished the work.他说他做完工作了。
He will say,"I have watered the flowers.”他会说:“我己经浇花了。”
→He will say he has watered the flowers.他会说他己经浇花了。
⒊ 指示代词、时间状语和地点状语的相应变化见下表:
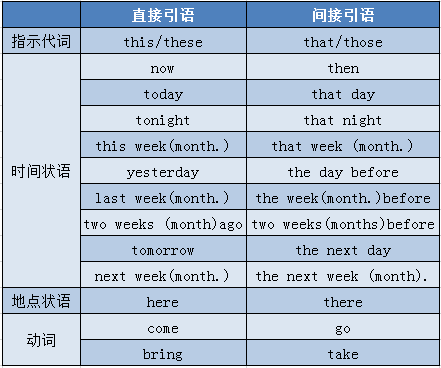
He said,"I met Mr.Smith this morning.”他说“我今天早晨见到史密斯了。”
→He said that he had met Mr.Smith that morning.他说他那天早晨见到史
密斯了。
He said,“We went to the cinema yesterday.”他说:“我们昨天去电影院了。”
→He said they had gone to the cinema the day before.他说前一天他们去电影院了。
Lily said,“I will come back next month.”莉莉说:“我下个月回来。”
→Lily said that she would go back the next month.莉莉说她下一个月就回去。
He said,“It is nine o'clock now.”他说:“现在九点了。”
→He said that it was nine o'clock then.他说那时九点了。
He said,"I haven't seen her today.”他说:“今天我没见到她。”
→He said that he hadn't seen her that day.他说那天他没有见到她。
She said,“I went there yesterday.”她说:“昨天我去了那儿。”
→She said that she had gone there the day.before.她说前一天她去了那儿。
She said,“Ill go there tomorrow.”她说:“明天我将去那儿。”
→She said that she would go there the next day.她说第二天她将去那儿。
He said,"My sister was here three days ago.”他说:“三天前我妹妹在这儿。”
→He said that his sister had been there three days before.他说三天前他妹妹在那儿。(here-there;ago-before)
She said,“I will come here this evening.”她说:“今晚我将来这儿。”
→She said that she would go there that evening.她说那晚她将去那儿。(come-go;here-there;this-that)
以上这些变化,要根据说话的具体时间和具体地点的情况而定,不可机械照搬。如果就在当地转述,here就不必改为there,come也不必改为go,如果就在当天转述,yesterday或tomorrow等时间状语也不必改变。直接引语中的一般过去时如与一个具体的过去时间状语连用,间接引语的一般过去时时态不变。
Father said,“I am free this afternoon”父亲说:“我今天下午有空。”
→Father said that he was free this afternoon.父亲说他今天下午有空。
He said,"I am going there tomorrow.”他说“我明天去那里。”
→He said that he was going there tomorrow.他说他明天去那里。
巧记:去掉引号加that,人称变化要灵活,时态向后退一步,状语变化按规定。
3
当直接引语是疑问句时
直接引语如为疑问句,改为间接引语时,须将疑问句的语序改为陈述句的语序。其人称、时态等相应的变化同上。
巧记:if(或whether)替引号,陈述语序要记牢。时态人称和状语要变化,千万别把它忘掉。
⒈ 直接引语是一般问句
变为间接引语时,须用连接词whether或if将其引出,使其成为间接引语的宾语从句。如果主句中的谓语动词为said,则将其改为asked。如果谓语动词后没有间接宾语,可以加上一个间接宾语me,him,her,them,us等。
She said,“Is your father an engineer?”她说:“你父亲是工程师吗?”
→She asked me whether my father was anengineer.她问我说我父亲是否是工程师。
The teacher said to Li Ming,“Have you finished your homework?”老师对李明说:“你做完作业了吗?”
→The teacher asked Li Ming whether he had finished his homework.老师问李明是否已做完作业了。
⒉ 直接引语是特殊问句
如果直接引语为特殊疑问句,改为间接引语时,仍用特殊疑问句中的疑问词what,where,when,who,how many作为连接词将其引出,构成间接引语中的宾语从句,但须将疑问式的动词改为陈述式。如果主句中的谓语动词为said,则将其改为asked。
巧记:直接去引号,陈述语序莫忘掉。助动do(does)、did,要去掉。
“What do you do every Sunday morning?”my friend said to me.我的朋友问我说,每星期天上午你做什么?
→My friend asked me what I did every Sunday morning.我的朋友问我每星期天上午我做什么。
“Where have you been,Li Ming?"the teacher asked.老师问道:“你上哪里去了,李明?”
→The teacher asked Li Ming where he had been.老师问李明曾去过哪儿。
I asked her,“How many English books will you read next term?”我问她说:“下学期你将读多少本英语书?”
→I asked her how many English books she would read the next term.我问她下学期将读多少本英文书。
“When did you get up this morning?"asked my father.我父亲问道:“今天早晨你什么时候起床的?”
→My father asked me when I had got up that morning.我父亲问我那天早晨我是什么时候起床的。
注意:直接引语里是:What's wrong with.....?/What's the matter?/What's the trouble?/What has happened?/等特殊疑问句时,间接引语的语序不变。
He said to her"What's the matter with you?”他问她“你怎么了?”
→He asked her what was the matter with her.他问她怎么了。
4
当直接引语是祈使句时
巧记:去掉引号要加to;ask,order须记住,直引若是否定式,not加在to前部。
转述祈使句时,要使祈使句的动词原形变为带to的不定式,并在不定式的前面根据句子的意思加上tell、ask、order等动词,如果祈使句为否定式,在不定式的前面加not。如果祈使句中有please一词,改为间接引语时,就将please去掉。成为:told(asked,ordered,warned)someone(not)to do something结构。
He said,“Sit down,please.”他说:“请坐。”
→He asked me to sit down.他让我坐下。
The teacher said,“Don't talk in class!”老师说:“上课不要讲话!”
→The teacher told us not to talk in class!老师要我们上课不要讲话。
The captain said to his men,“Fire!”上尉对他的士兵们说“开火!”
→The captain ordered his men to fire.上尉命令他的士兵们开火!
The policeman said to the children,"Don't play football in the middle of the street.”警察对孩子们说:“别在马路中间踢足球。”
→The policeman warned the children not to play football in the middle of the street.警察警告孩子们不要在马路中间踢足球。

1
and连接的句子
在由and连接的句子中,为避免重复常省略一些重复的词或词组。
⒈ 省略共同的主语或宾语。
如:Mr. Smith picked up a coin in the road and (Mr.Smith)handed it to a policeman.
⒉ 若主语不同而谓语助动词,情态动词相同,则省略后面的助动词或情态动词。
如:Jack must have been playing football and Mary (must have been)doing her homework.
⒊ 若主语与谓语动词相同,则省略后面的主谓成分。
如:His advice made me happy, but (his advice made) Jim angry.
⒋ 若主语不同,但主要动词及后续部分相同,则省略主要动词及后续部分。
如:I was born in winter in 1988 and Bob ( was born in winter) in 1989.
⒌ 省略重复的介词,连词及后续部分。
如:He was late because he had overslept and ( because he had) missed the train.
2
状语从句的省略
⒈ 在when, while, whenever, till, as soon as, if, unless, as if, though, as, whether等引导的状语从句中,若谓 语有be, 而主语有跟主句主语相同或是it时,则从句的主语和be常被省略。
如:As (he was) young, he was a store-keeper.
His opimion, whether (it is) right or wrong , would be considered.
⒉ 在as, than, however, whatever, no matter what等引导的从句中常省略某些成分。
如:Anyone, no matter who (he is), may point out our shortcomings.
I can only do it the way as ( I was) told to (do it that way).
⒊ 虚拟条件句常省略if, 将were, had, should 提前构成部分倒装。
如:Should there be a flood =(If there should be a flood), what should we do?
⒋ 有些状语从句置于句末,可作句尾省略,有时可省略整个从句。
如:John will go there if my brother will (go).
I would have come yesterday (if I had wanted to ).
3
定语从句和名词性从句中的省略
⒈ 在限定性定语从句中,作宾语用的关系代词whom, which, that可省略;在以the same…as和such as引出的某些定语从句中,也可省略与主句相同部分。
如:The girl (whowhom hat) the teacher spoke to is Liu Ying.
I don't like such books as this (is).
⒉ 定语从句中的“主语+系动词be”可以省略。
如:The goods (which were) ordered last month haven't arrived yet.
⒊ 在know, think, consider, suppose, find, believe, say, decide等动词后面所接的宾语从句中,连词that可以省略;若带有多个宾语从句,只有第一个that可省略,其余的则不能。
如:I think (that) it will clear up(转晴)this afternoon.
He said(that) the text was very important and that we should learn it by heart.
⒋ 由which, when, where, how和why引导的宾语从句,可全部或部分省略。
如:He will come back, but he doesn't know when ( he will come back).
⒌ 在与suggest, request, order, advise等词相关的名词性从句中,须用虚拟语气形式'should+动词原形,should可省略。
如:The officer ordered that his men (should) fire.
It is suggested that we (should) go to see the flim.
4
复合句中特殊的省略现象
⒈ 主句省略多用于句首,在答句中,主句或者一些成分可全部省略。
如:(It is a) Pity that I didn't go to mary's birthday party yesterday.
⒉ 省略一个从句或从句的一部分,可用so或not代替。
如:—She may not be free today.
—If so (so=she is not free today), we will have to report the manager.
—Is he feeling better today?
—I'm afraid not(not=he isn't feeling better today).
5
动词不定式省略,只保留to的场合
⒈ 不定式作某些动词的宾语时,常见动词如like, love, care, hope, wish, expect, afford, forget, prefer, refuse, mean, try, oblige(强迫),advice, persuade, agree, want, remember, manage等。
如:You can do it this way if you care to.
—You should have thanked her before you left.
—I mean to , but when I was leaving I could't find her anywhere.
⒉ 不定式在句中作某些动词后的宾补或主补时,常见的有ask, tell, advise, force, persuade, wish, allow, permit等。
如:She wants to come but her parents won't allow to.
⒊ 不定式在句中作某些形容词的状语时,常见形容词如happy, glad, eager, anxious, willing, ready等。
如:I think she should get a job, but you can't force her to if she's not ready to
—I'll be away on a business trip. Could you mind looking after my cat?
—Not at all. I'd be happy to.
⒋ 不定式作某些复合谓语时,常见结构如be able to, be going to , have to, ought to, used to等。
如:He doesn't like fish but he used to.
注意,当省略的内容是作动词用的have或be的任何形式时,to 后面保留原形have或be.
如:He didn't come, but he ought to have.
Alice is not what she used to be.
6
动词不定式符号to 的省略
⒈ 主语部分有to do, 系动词是 is或was时,作表语的不定式通常省略to.
如:The only thing you have to do is (to) press the button.
⒉ 作介词but, except, besides的宾语时,前面有实义动词do时,常省略不定式符号to.
Tom had nothing to do besides answer betters this morning.
⒊ 当两个或多个不定式并列时,其后的不定式符号可省略,但有对比关系时则不省略。
如:It is easier to make a plan than to carry it out.
⒋ 在see, watch, notice, hear, listen to, look at, feel, have make, let, leave, observe等词后作宾语补足语时,省略不定式符号to;Why (not)do结构中不定式不带to.
如:Did you notice her enter the room?
why not join us?
7
介词的省略
⒈ 一些常和动名词、形容词一起搭配的介词常省略,而保留其后的 动名词,常见的句型有spend/waste time(in)doing, lose no time(in)doing, have difficult/trouble (in) doing, be busy (in) doing, stop/prevent sb. (from) doing 等。
如:The heavy rain prevented him (from) arriving there on time.
She lost no time(in) giving the patient first aid.
⒉ 表示时间的介词at, on和in 用在next, last, this, these, yesterday, tomorrow, one, any, every, each, some, all等词之前,一般皆省略,表示一段时间状语之前的for 也可省略。
如:We go to school every day except Sunday.
We have been here (for) three weeks.(否定句中不能省略for)
⒊ 表示行为方式的in在in this way, in the same way, in another way等词组中,经常被省略。
如:He did it (in) this way.
8
会话中的省略
省略在会话中应用广泛,无论是回答别人问题,还是在接别人说话时都会发生,否则就觉得累赘。
如:—Do you like this shirt?
—Yes, (I like it) very much.
(Come) This way,please.
—What do you think made Mary so upset?
—Losing her bicycle(made her so upset).

1
概念
英语的基本语序是“主语+谓语”,如果将谓语的一部分或全部放在主语之前,这种语序叫装。倒装既是一种语法手段,也是一种修辞手段,用于表示一定的句子结构或强调某一句子成分。
2
倒装的种类
如果将句子的主语和谓语完全颠倒过来,这称之为完全倒装。
如果只将助动词或情态动词移至主语之前,谓语的其他部分仍保留在主语的后面,这称之为部分倒装。
⒈ 完全倒装
① 完全倒装是将谓语的全部放在主语之前,此结构通常只用于一般现在时和一般过去时两种。
如:On her left sat her husband.她左边坐着她丈夫。
Here is the book you want.你要的书在这儿。
Down went the small boat.小船沉下去了。
② 常见的完全倒装结构
⑴ there be句型。
如:desk.桌上有一个手机和一些书。
There are thousands of people gathering on the square.广场上聚集着成千上万的人
注意引导词there还可以接appear,exist,lie,remain,seem,stand,live等词。
There lived an old fisherman in the village.村里住着一位老渔夫。
There stand two white house by the river.河滨立着两座白房子。
There existed some doubt among the students.学生中有些怀疑。
⑵ 用于here,there,now,thus,then+动词+主语的句型中(谓语动词多为be,go,come等)。
如:Here comes the bus.汽车来了。
There goes the bell.铃响了。
Now comes my turn.轮到我了。
Then came the order to take off.起飞的命令到了。
⑶ 以out,in,up,down,off,away等副词开头,谓语动词是表示“移动”的go,come,leave等句子里。
如:Away went the crowd one by one.人们一个一个地离去。
In came a stranger in black.进来了一位穿黑衣的陌生人。
Down fell the leave.,树叶掉了下来。
注意在完全倒装的结构里,如果主语是人称代词,则用正常语序。
如:Out she went.她走了。
Here we are.我们到了。
⑷ 表示地点的介词词组位于句首,谓语动词是表示“存在”之意的be,lie,stand,exist等句子中。
如:South of the lake lies a big supermarket.湖泊的南边是一个大超市。
20miles east of our school lies a modern swimning pool.我们学校向东20英里有一个现代化的游泳池。
On the floor were piles of old books,magazines and newspapers.地板上是一堆堆旧的书报杂志。
⑸“表语+系动词+主语”结构。
如:Lucky is she who was admitted to a famous university last year.她很幸运,去年被一所名牌大学录取。
Gone are the days when he was looked down upon.他被人看不起的日子一去不复返了。
Present at the meeting are some well-known scientists.一些知名的科学家出席了会议。
⒉ 部分倒装
① 部分倒装是指将谓语的一部分,如助动词或情态动词,移至主语之前。
如:Only by working hard can one succeed.只有努力才能成功。
Never have I seen her before.我以前没见过她。
提示:如果句中的谓语没有助动词或情态动词,则需添加助动词do,does或did,并将其置于主语之前。
Well do I remember the day I joined the League.入团的那一天,我记忆犹新。
Little did I think that he could be back alive 我没有想到他竟能活着回来。
② 常见的部分倒装结构
含有否定意义的副词或连词(如 not,seldom,little,hardly,never,rarely,nowhere等)放在句首时。
如:He can not speak a single word of English.
→Not a single word of English can he speak.他连一个英语单词都不会说。
He cares little about his clothes.
→Little does he care about his clothes.他不在乎穿着。
I have never seen hin before.
→Never have I seen him before.
→Never before have I seen him.我以前没见过他。
The mother didn't leave the room until the child fell asleep.
→Not until the child fell asleep did the mother leave the roon.孩子睡着了,妈妈才离开房间。(Not until引出的主从复合句中,主句倒装,从句不倒装。)
Churchill wes not only a statesman,but a poet
→Not only was Churchill a statesman,but a poet.丘吉尔不仅是个政治家,而且还是个诗人。
I shall by no means give up.
→By no means shall I give up.我决不放弃。
必背:表示“网刚…….就……的倒装结构
如:Hardly had he started to leave when it began to rain.他刚要离开,天就下起了雨。
Scarcely had he sat down when his mobile phone rang.他刚坐下,手机就响了。
No sooner had he handed in his paper than he realized his mistakes.他刚交卷就意识到出错了。
3
副词only+状语放在句首时
only+状语从句,从句不倒装,主句倒装
如:Only then did I see life was not easy.只有那时我才知道生活是不易的。
Only in this way can you use the computer well.只有用这种方法你才能把电脑学好。
0nly when he is seriously ill does he ever stay in bed.只有他病重时,他才待在床上。
4
So引导的倒装句
so作“也”讲时,引导的句子用倒装语序,表示前面所说的肯定情况也适用于另一人(或物)。其句型是:So+be(have,助动词或情态动词)+主语。
如:She has been to Tokyo.So have I.她去过东京,我也去过。
He can send emai ls to his former classnates.So can she他能电子邮件给以前的同学,她也能。
He went to the film last night.So did I.昨天晚上他去看电影了,我也去了。
注意:如果对前面所说的内容,加以肯定,或不作“也”讲而只起连词作用,表示一种结果的意思,那不倒装。
—Jack won the first prize in the contest.杰克在比赛中获一等奖。
—So he did.确实是的。
—It is cold today.今天很冷。
—So it is and so was it yesterday.确实是很冷,昨天也很冷。
His mother told hin to go to the film.So he did.他母亲叫他去看电影,他就去了。
5
neither/nor引导的句子
neither/nor引导的句子用倒装语序,用于对前面所说的否定内容表示同样的看法
如:I cannot swim.Neither can he.我不会游泳,他也不会。
注意:如果前面所说的内容既有肯定又有否定,或前后的谓语动词形式不一致时,用“It is the same with+主语”结构或用“Soit is with+主语”结构。
如:He worked hard,but didn't pass the exam.So it was with his sister.他很努力,但没有通过考试。他妹妹也是这样。(既有肯定又有否定)
She is a teacher and she enjoys teaching.So it is with MrLi.她是老师,热爱教书。李先生也是这样。(谓语一个是系动词,一个是行为动词)
6
“so..…that..…和“such..that..”结构
“so..…that..…和“such..that..”结构中的so或such位于句首时。
如:He was so excited that he could not say a word.
—So excited was he that he could not say a word.他如此激动以至于一句话都说不出来。
His anger was such that he lost control of himself.
—Such was his anger that he lost control of himself.他是如此地生气,以至于他不能控制自己了。
7
用于省略if的虚拟语气条件状语从句
如:Had you received your lessons,you might have passed the exam.
Were I to do the work,I should do it some other way.
Should I be free tomorrow,I could go with you.
8
as/though引导的让步状语从句中的倒装
⒈ 表语提前,构成倒装。
如:Though she is very pretty,she is not clever.
→Pretty though she is,she is not clever.虽然她很漂亮,但是她不聪明。
Although it may appear strange,it is true.
→Disabled as he was,he tried his best to serve the people.虽然他残疾了,但他仍尽力为人民服务。
Although he is a child,he speaks fluent English.
→Child as he is,he speaks fluent English.虽然他是个孩子,但能讲流利的英语。(名词单数前不用不定冠词a)
Though he is the shortest,he is the richest of the three.
→Shortest as he is,he is the richest of the three.虽然他是三个人中最矮的,却是最富有的。 (形容词最高级前去定冠词 the)
⒉ 动词提前,构成倒装。
Though they searched,they could not find anything in the house.
→Search as they did,they could not find anything in the house.虽然他们搜遍了,却没在房子里找到任何东西。
Though I failed,I would try again.
→Fail as I didI would try again.尽管我失败了,但我还要再试。
Though she may try again,she won't pass it.
Try as she may,(she won't pass it.尽管愿意再试,她还是不会通过的。
⒊ 副词提前,构成倒装。
Though he tried hard,he couldn't pass the exam.
→Hard as he tried,he couldn't pass the exan.尽管他努力了,他还没有通过考试。
Though I listened attentively,I still couldn't understand what he said at the meeting.
→Attentively as I listened,I still couldn't understand what he said at the meeting.尽管我专心听了,我还是不懂他在会议上说的话。
Though he ran the fastest,he still didn't catch the train.
→Fastest as he ran,he still didn't catch the train.尽管他跑得最快,仍没有赶上火车。 (副词最高级前不用定冠词 the)

1
强调句句型的种类及句型
⒈ 陈述句的强调句型:It is/ was + 被强调部分(通常是主语、宾语或状语)+ that/ who(当强调主语且主语指人)+ 其他部分。
如:It was yesterday that he met Li Ping.
⒉ 一般疑问句的强调句型:同上,只是把is/ was提到it前面。
如:Was it yesterday that he met Li Ping?
⒊ 特殊疑问句的强调句型:被强调部分(通常是疑问代词或疑问副词)+ is/ was + it + that/ who + 其他部分?
如:When and where was it that you were born?
⒋ 强调句例句:针对I met Li Ming at the railway station yesterday.句子进行强调。
① 强调主语:It was I that (who) met Li Ming at the railway station yesterday.
② 强调宾语:It was Li Ming that I met at the railway station yesterday.
③ 强调地点状语:It was at the railway station that I met Li Ming yesterday.
④ 强调时间状语:It was yesterday that I met Li Ming at the railway station.
⑤注意:构成强调句的it本身没有词义;强调句中的连接词一般只用that、who,即使在强调时间状语和地点状语时也如此,that, who不可省略;强调句中的时态只用两种,一般现在时和一般过去时。原句谓语动词是一般过去时、过去完成时和过去进行时,用It was…,其余的时态用It is…
2
not … until … 句型的强调句
⒈ 句型为:It is/ was not until + 被强调部分 + that + 其他部分
如:普通句:He didn't go to bed until/ till his wife came back.
如:强调句:It was not until his wife came back that he went to bed.
⒉ 注意:此句型只用until,不用till。但如果不是强调句型,till, until可通用;因为句型中It is/ was not …… 已经是否定句了,that后面的从句要用肯定句,切勿再用否定句了。
3
谓语动词的强调
⒈ It is/ was …… that …… 结构不能强调谓语,如果需要强调谓语时,用助动词do/ does或did.
如:Do sit down. 务必请坐。
He did write to you last week. 上周他确实给你写了信。
Do be careful when you cross the street. 过马路时,务必(千万)要小心啊!
⒉ 注意:此种强调只用do/ does和did,没有别的形式;过去时用did,后面的谓语动词用原形。
4
强调句的疑问句
⒈ 强调结构的疑问形式:强调一般疑问句中的某一成分时,要在主 句中用一般疑问句的顺序。
如:Was it you that/who broke the window?
Was it in the war that he lost his son?
⒉ 强调特殊疑问句中的疑问词,其结构模式是:“疑问词+is/was+it +that。”它同感叹句 的强调模式极其相似,首先将疑问句开头的部分作为强调部分,套入强调结构,然后再将其变为疑问句。
如:Where were you born?
→Where was it that you were born?
What did you want to see?
→What was it that you wanted to see?
How many people are being trained for the special work?
→How many people is it that are being trained for the special work?
5
强调句型中的主谓一致
⒈ 被强调的成分为原句的主语时,that/who之后的谓语动词应与被强调的名词或代词在人称和数方面保持一致关系,从而选用恰当的动词形式。
如: It is you who/that are wrong.
It is I who/that am answering the question.
⒉ 但是如果被强调的部分是人称代词,按理应用人称代词主格形式,但在口语或非正式文 体中也可以用其宾格形式,此时that/who的谓语动词要用单数第三人称形式is或was。
如: It is me who is being asked the favor.
⒊ 另在Itis/was…,not…that…句型中,其谓语动词应与肯定部分的词保持一致关系。
如: It is my brother,not I that studies in that school.
It is you,not your sister that are in charge of the company.
6
感叹句的强调结构
既要体现强调句型的形式特征,又要体现感叹句的自然语序。
如: How happy he looks!→How happy it is that he looks!
What a clever boy he is!→What a clever boy that he is!

1
概念
虚拟语气:表示动作或状态不是客观存在的事实,而是说话人的主观愿望、假设或 推测等。
如:If I were you,I should study English.如果我是你,我就学英语了。
May you succeed!祝您成功!
2
虚拟语气在条件从句中的用法
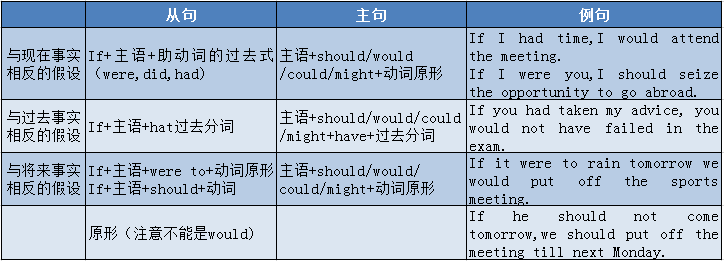
条件句有两类,一类是真实条件句,一类是虚拟条件句。
⒈ 真实条件句
如果假设的情况是有可能发生的,就是真实条件句。在这种真实条件句中的谓语用陈述语气。
如:If it doesn't rain tomorrow,we will go to the park.如果明天不下雨,我们就去公园。
⒉ 虚拟条件 句
如果假设的情况是过去或现在都不存在的,或将来不大可能发生的,则是虚拟条件句。
如:If he had seen you yesterday,he would have asked you about it.如果他昨天见到你,他会问你这件事的。(事实上他昨天没见到你,因此也未能问你这件事。)
⒊ 错综时间条件句
当条件状语从句表示的行为和主句表示的行为所发生的时间不一致时,被称为错综时间条件句,动词的形式要根据它表示的时间作出相应的调整。
如:If you had followed my advice just now you would be better now.
If you had studied hard before,you would be a college student now.
⒋ if省略句
在条件句中可以省略if,把were,had,should提到句首,变成倒装句式。
如:If I were at school again,I would study harder.
→Were I at school again,I would study harder.如果我还有上学的机会,我会更加努力学习。
If you had come earlier,you would catch the bus.
→Had you come earlier,you would catch the bus.如果你来得早点,你就能赶上公共汽车。
If it should rain tomorrow we sould not go climbing.
→Should it rain tomorros iwe would not go climbing.如果明天下雨的话,我们就不能登山去了。
⒌ 用介词代替条件状语从句
常用的介词有with,without,but for。
如:What would you do with a million dollars?(=if you had a nillion dollars)如果你有100万元,你会做什么?
We couldn't have finished the work ahead of time without your help(=if we hadn't got your help)没有你的帮助,我们不可能提前完成这项工作。
Without your help we couldn't have finished the work ahead of time.
=But for your help,…
=If it had not been for your help,…
=Had it not been for you help,…
没有你的帮助,我们不可能提前完成这项工作。
⒍ 含蓄条件句
有时在虚拟语气中并不总是出现if引导的条件句,而是通过其他手段来代替条件句。
如:I was ill that day.Otherwise, would have taken part in the sports meeting.(副词)
He telephoned to inform me of your birthday,or I would have known nothing about it.(连词)
A man who stopped drinking water would be dead in about seven days.(定语从句)
I might hawe given you nore help,but I was too busy.(连词)
Everything taken into consideration they would have rai sed their output quickly.(独立主格结构)
精品干货,点击阅读
● 高考英语大纲规定的24个语法梳理(一)
● 高考英语大纲规定的24个语法梳理(二)
● 高考英语大纲规定的24个语法梳理(三)
● 高考英语大纲规定的24个语法梳理(四)
● 高考英语大纲规定的24个语法梳理(五)
▐标签:高考英语 精品干货
▐ 来源: 维克多英语 谨以致谢,如有侵权,请立即联系删除
责任编辑:
本文网址:http://jyqqw.com/waiyu/6705.html
声明:本站原创/投稿文章所有权归中国在线学习网所有,转载务必注明来源;文章仅代表原作者观点,不代表中国在线学习网立场;如有侵权、违规,可直接反馈本站,我们将会作删除处理。
上一篇: 论“散装英语”,我只服沈腾!
网友评价

来自黑龙江省宁安市的热心网友评价:
还不错哦
 1057
1057

来自安徽省宁国市的热心网友评价:
太优秀了!很多观点都记下了
 1057
1057

来自湖南省湘潭市的热心网友评价:
好棒!
 1057
1057

来自四川省乐山市的热心网友评价:
厉害
 1057
1057

来自陕西省商洛市的热心网友评价:
见识了!
 1057
1057
留学
更多>>-

澳大利亚新洲留学 如何选择合适的留学院校?
2020-11-11
-

大量留学生归国求职 就业压力倍增 如何高效找到好工作?
2020-11-09
-

英语专业海外留学应该如何选择专业?那些专业较为合适?
2020-11-06
-

美国留学热门专业排行 全方面解析不同专业的就业形势
2020-11-05
-

日本留学生生活攻略 了解这些可以让你的留学生活更美好
2020-10-29









